Ви не увійшли.
- Теми: Активні | Без відповіді
- Форум
- » Проекти
- » Управление вентилятором радиатора автомобиля, разработка.
- » Відповісти
Відповісти
Огляд теми (нові повідомленні вгорі)
- yarikne
- 2017-05-21 21:48:32
Процесс не стоит на месте. Прототип уже установлен на подопытный автомобиль.
Уже реализован шим на частоте 25гц. который необходим для управления заводским блоком управления вентиляторами(Штатный на современных мерседесах и фольцвагенах).
Пока открыт вопрос с входами для запуска вентиляторов от блока кондиционера.
Довесил датчик температуры LM75 и ЛСД 16*2 для отладки.
Спасибо NoName, библиотеку и код писал/правил он.
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* "THE BEER-WARE LICENSE" (Revision 00):
* <devgate.info эт gmail.com> wrote this file. As long as you retain this notice you
* can do whatever you want with this stuff. If we meet some day, and you think
* this stuff is worth it, you can buy me a beer in return.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Date create: 2017.05.08
* Date change: 2017.05.09
* Date change: 2017.05.22
* Date change: 2017.05.30 add key function control
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x3F, 16, 2);
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LM75.h>
LM75 sensor(0x48); // initialize an LM75 object
//#define USE100Hz
char debug_str[100];
#define START_SIGNAL 50
#define KEY1_SIGNAL 50
#define KEY2_SIGNAL 10
#ifdef USE100Hz
#define MAX_SIGNAL 9000
#define MIN_SIGNAL 100
#include <dgm_pwm25.h>
#else
#include <dgm_pwm25.h>
#define MAX_SIGNAL 39000
#define MIN_SIGNAL 1000
#endif
#define USE_FILTER16
#define DEBUG
//#undef DEBUG_PWM
//#define DEBUG_TEST_SYSTEM
#define DEBOUNCE_TIME 100
#define TASK_PROCESS_TIME 1000
int KEY1 = 7;
int KEY2 = 8;
int test_power;
int lcdPower;
typedef enum {
TIMER_EXE = 0,
TIMER_DISABLED = 1,
TIMER_RUN = 2,
} TE_TIMER;
typedef struct
{
int pin_number;
int time_debounce;
unsigned long time_press ;
unsigned long time_release;
unsigned long time_last_press;
unsigned long time_last_release;
int press_level_detect;
bool status_press;
bool status_release;
bool interrupt_press;
bool interrupt_release;
bool need_release;
bool execute;
} tdpkey;
tdpkey key_1;
tdpkey key_2;
// Change these two numbers to the pins connected to your encoder.
// Best Performance: both pins have interrupt capability
// Good Performance: only the first pin has interrupt capability
// Low Performance: neither pin has interrupt capability
// Encoder myEnc(2, 3);
// avoid using pins with LEDs attached
Servo esc;
void setup() {
lcd.begin();
lcd.backlight();
Wire.begin();
esc.attach(9, MIN_SIGNAL, MAX_SIGNAL);
esc.write ( START_SIGNAL );
key_1.time_debounce = 50;
key_1.pin_number = 7;
key_1.press_level_detect = HIGH;
key_2.time_debounce = 50;
key_2.pin_number = 8;
key_2.press_level_detect = HIGH;
pinMode(key_1.pin_number, INPUT);
pinMode(key_2.pin_number, INPUT);
pinMode(KEY1, INPUT);
pinMode(KEY2, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Start DGM_PWM_25Hz");
}
// long oldPosition = 0xFFFF;
// long newPosition;
long _PWM = 0;
// http://forum.arduino.ua/viewtopic.php?pid=3088#p3088
// GREEN
// CHANGE
bool KEY1CONTROL()
{
static bool key_pressed;
static uint8_t debounce_timer;
if (key_pressed == digitalRead(KEY1)) {
key_pressed = !key_pressed;
debounce_timer = DEBOUNCE_TIME;
}
else if (debounce_timer && !--debounce_timer && key_pressed)
return true;
return false;
}
bool KEY2CONTROL()
{
static bool key_pressed;
static uint8_t debounce_timer;
if (key_pressed != !digitalRead(KEY2)) {
key_pressed = !key_pressed;
debounce_timer = DEBOUNCE_TIME;
}
else if (debounce_timer && !--debounce_timer && key_pressed)
return true;
return false;
}
TE_TIMER system_delay_uint32 ( unsigned long *timer , unsigned long shift )
{
if ( *timer > 0 )
{
if (*timer > shift )
{
*timer -= shift;
return TIMER_RUN;
}
else
{ // save delta time
*timer = ( shift - *timer );
return TIMER_EXE;
}
}
return TIMER_DISABLED;
}
typedef struct
{
int voltage;
int power;
} td_table_unit;
td_table_unit power_table[] =
{
{ 5000, 90 },
{ 2200, 90 },
{ 2100, 85 },
{ 2000, 75 },
{ 1950, 60 },
{ 1900, 40 },
{ 1850, 30 },
{ 1800, 10 },
{ 0, 10 }
};
int voltage_array_pos;
int voltage_array_data[16];
bool enabled_voltage_array = false;
int need_system_power;
int linear_table_interpolation ( int X, int pos )
{
long XXX;
int ret;
long X1, fX1;
long X2, fX2;
if ( pos == 0 ) return ( power_table[0].power ) ;
X1 = power_table[pos-1].voltage;
fX1 = power_table[pos-1].power;
X2 = power_table[pos].voltage;
fX2 = power_table[pos].power;
XXX = fX1 + (fX2 - fX1)*(X - X1)/(X2 - X1);
// Serial.print (" X1: "); Serial.print (X1); Serial.print (" fX1: "); Serial.println (fX1);
// Serial.print (" X2: "); Serial.print (X2); Serial.print (" fX2: "); Serial.println (fX2);
ret = (int) XXX;
if ( ret < 0 ) ret = 0;
if ( ret > 100 ) ret = 100;
return ret;
}
void clear_fkey_interrupt ( tdpkey *pkey )
{
pkey->interrupt_release = false;
pkey->interrupt_press = false;
pkey->need_release = true;
}
//------------------------------------
void fKey (tdpkey *pkey, int time_elapsed )
{
if ( digitalRead( pkey->pin_number) == pkey->press_level_detect )
{
pkey->time_press += time_elapsed;
}
else
{
pkey->time_release += time_elapsed;
}
// кнопка была отжата
if ( pkey->time_release > pkey->time_debounce )
{
if ( pkey->status_release == false )
{
pkey->time_press = 0;
pkey->status_release = true;
pkey->status_press = false;
pkey->interrupt_press = false;
if ( pkey->need_release == false )
{
pkey->interrupt_release = true;
}
pkey->need_release = false;
pkey->time_last_release = pkey->time_release;
pkey->time_release = 0;
#ifdef DEBUG
sprintf ( debug_str,"key_release"); Serial.println ( debug_str );
#endif
}
}
if ( pkey->time_press > pkey->time_debounce )
{
if ( pkey->status_press == false )
{
pkey->status_press = true;
pkey->need_release = false;
pkey->time_release = 0;
pkey->status_release = false;
pkey->interrupt_press = true;
pkey->interrupt_release = false;
pkey->time_last_release = pkey->time_release;
pkey->time_release = 0;
#ifdef DEBUG
sprintf ( debug_str,"key_press"); Serial.println ( debug_str );
Serial.println ( pkey->time_release );
#endif
}
}
return;
}
void loop() {
static unsigned long task_time;
static unsigned long key_time_start_press;
static unsigned long key_time_start_unpress;
TE_TIMER status;
static unsigned long hw_old_system_timer = 0;
unsigned long hw_current_system_timer = 0;
unsigned long delta_task_timer;
int position = 0;
unsigned long test;
int sensorValue = 0;
static int raw_sensorValue = 0;
static int delta = 0;
long voltage;
int power = 95;
int now_status = 0;
long new_duty_cycle = 0;
// Convert the analog reading (which goes from 0 - 1023) to a voltage (0 - 5V):
int preset_power = 0;
hw_current_system_timer = millis();
delta_task_timer = hw_current_system_timer - hw_old_system_timer;
hw_old_system_timer = hw_current_system_timer;
status = system_delay_uint32 ( &task_time, delta_task_timer );
fKey (&key_1 , delta_task_timer );
fKey (&key_2 , delta_task_timer );
#ifndef DEBUG_TEST_SYSTEM
raw_sensorValue = analogRead(A0);
#else
// raw_sensorValue &= 0x3FF;
if ( raw_sensorValue > 1024 ) raw_sensorValue = 0;
#endif
#ifdef USE_FILTER16
long sum = 0;
voltage_array_data[voltage_array_pos] = raw_sensorValue;
voltage_array_pos++;
if ( voltage_array_pos >= 16 )
{
enabled_voltage_array = true;
voltage_array_pos = 0;
}
if( enabled_voltage_array )
{
for ( int foo = 0; foo < 16; foo++ )
sum += voltage_array_data[voltage_array_pos];
sum >>= 4; // деление на 16
sensorValue = sum;
}
else
{
sensorValue = raw_sensorValue;
}
#else
sensorValue = raw_sensorValue;
#endif
voltage = sensorValue * (5000.0/1023.0);
// voltage = map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 5000);
lcdPower = map(need_system_power, 0, 100, 100, 0);
// print out the value you read:
if ( key_1.status_press ) now_status |= 0x0001;
if ( key_2.status_press ) now_status |= 0x0002;
if ( now_status&0x0001 ) preset_power = KEY1_SIGNAL;
else if ( now_status&0x0002 ) preset_power = KEY2_SIGNAL ;
#ifdef DEBUG_PWM
if ( test_power > 100 ) test_power = 0;
esc.write ( test_power );
power = test_power;
#else
if ( voltage < 0 ) voltage = 0;
for ( position = 0 ; ; position++ )
{
if ( voltage >= power_table[position].voltage )
break;
}
need_system_power = linear_table_interpolation (voltage,position);
#endif
if ( preset_power > need_system_power ) esc.write ( preset_power );
else esc.write ( need_system_power );
#ifdef DEBUG
switch ( status )
{
case TIMER_EXE:
case TIMER_DISABLED:
task_time += TASK_PROCESS_TIME;
#ifdef DEBUG_TEST_SYSTEM
raw_sensorValue += 1;
#endif
test_power++;
Serial.print (digitalRead(KEY1));
Serial.print (digitalRead(KEY2));
if ( now_status & 0x0001 )
Serial.print (" D7: ON ");
else Serial.print (" D7: OFF ");
if ( now_status & 0x0002 )
Serial.print ("D8: ON ");
else Serial.print ("D8: OFF ");
Serial.print ("ADC: ");
Serial.print (sensorValue);
Serial.print (" ");
Serial.print ("V: ");
Serial.print (voltage);
Serial.print (" ");
Serial.print ("p: ");
Serial.println (lcdPower);
// get temperature from sensor
// Serial.print("Current temp: ");
// Serial.print(sensor.temp());
// Serial.println(" C");
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("Sens:");
lcd.print(voltage);
lcd.print("V ");
if ( now_status & 0x0001 )
lcd.print("1:ON");
if ( now_status & 0x0002 )
lcd.print("2:ON");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("FAN:");
lcd.print(lcdPower);
lcd.print("% ");
lcd.print("T:");
lcd.print(sensor.temp());
lcd.print("C");
//delay(150);
/*
Serial.print (" ");
test = esc.readMicroseconds();
Serial.print ("t: ");
Serial.print (test);
Serial.print(" ");
test = esc.read ();
Serial.print ("ms: ");
Serial.println (test);
*/
break;
case TIMER_RUN:
break;
}
#endif
}- NoName
- 2017-05-08 23:22:00
что то я переоценил свои силы, в 15 минут не вложился ) пока нашел этот дурацкий шуп ...
в общем прототип ушел на мыло )
servo - классический пример прогромного таймера, сделан с использованием аппаратного таймера для малых частот оличное решение
но по правильному лучше бы исправить analogwrite, но это наверное прийдется в дебри ардуино лезть.
либо после инициализации исправлять,
но мы так делать не будем ) мне привезли десяток робуст от фрискайла, на мои поворотники. харлеевские (если заказчик начнет отвечать в вайбер ), лодку то и на ваш прокт можно что то найти, это industrial mcu, не automotive но тоже хороши, и не только с пивом пойдут )
- yarikne
- 2017-05-08 22:42:49
Мыло активно, ноги, какие вам удобно.
По кнопкам все верно.
Аварийная работа 95% Скважность
Блок управления силовой, сам плавно все делает, тем более вентиляторы довольно инерционны.
- NoName
- 2017-05-08 22:36:06
"подстроечник" нету )
есть сотня 0805 резисторов, но на них неудобно делители набивать.
Вы забыли указать какие значения при авариной работе . например нет напруги, и на момент старта.
25 Гц сделал
#define INTERVAL_SIGNAL 40000
#define MAX_SIGNAL 36000
#define NETRUAL 20000
#define MIN_SIGNAL 4000
какие номера ног вы под кнопки выбрали?
по кнопкам
пока кнопка нажата ( + уровень ) устанавливает пресет по скорости вращения,
я бы вам рекомендовал плавную регулировку смены скважности
мыло ваше активно? код пришлю
- yarikne
- 2017-05-08 19:08:01
Не пойму зачем регулируемый источник? Для имитации можно взять любой подстроечник, я использую 10к. Средняя нога выход крайние питание.
Датчик - термистор, подключенный как плечо делителя напряжения, вторая половина плеча в ЭБУ. Физически расположен на корпусе термостата, на выходе из него. На датчик приходит масса ЭБУ и "подтяжка 5 вольт". Напряжения снимальсь ардуинкой:
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0);
// Convert the analog reading (which goes from 0 - 1023) to a voltage (0 - 5V):
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// print out the value you read:
Serial.println(voltage);
типа так.
Всего на двигателе 3 датчика температуры, один на ЭБУ двигателя, второй на ЭБУ клмат контроля и третий на стрелку в панеле приборов. Я тупанул и подключился к датчику климата, не знаю на сколько это кретично, но на многих авто, вентилятором охлаждения ОЖ управляет именно климат.
Можно конечно и собрать новые данные, нужно подумать.
- NoName
- 2017-05-08 15:36:04
благодарю
2 кнопки найду )
поищу регулируемый источник
но есть вопрос
как подключался датчик, как напряжение смотрели? и какая схема включение? кто то еще пользуется с електроники авто этим датчиком?
- yarikne
- 2017-05-08 14:53:02
Поделюсь и помогу Пете с удовольствием.
На счет точности установки скважности и частоты не знаю, нужно эксперементировать.
Думаю, что 5 ступенек скважности будет достаточно, 30% 50% 60% 80 и 90 (100 - не ставим, это аварийный режим, типа короткое замыкание управляющей линии на + или -).
Было-бы неплохо не энкодер, он не к чему, а напряжение на А0 соответствующие диапазонам.
от 5в до-2,1в - 10% (вентилятор выключен, если их нет, то он аварийно включается)
2в -30%;
от 2в до 1,95в-50%;
1,96в-1,90в - 60%;
1,89в-1,84в -80%;
и ниже 1,84в пусть гудит на всю, 90%.
Ну и еще нужно 2 цифровых входа, при подаче на один + вентилятор должен включаться на 50% при любых условиях, а второй на 90% - Это для работы кондиционера.
Это все цифры с головы, я какое-то время ездил с 16*2 возле спидометра и наблюдал за напряжением на датчике температуры.
- NoName
- 2017-05-08 11:40:01
http://www.atmel.com/Images/Atmel-7766-8-bit-AVR-ATmega16U4-32U4_Datasheet.pdf
меня к сожалению пробивает поменторствовать, старею )
но сегодня не тот вариант
самым быстрым решением - сделать вам код, но фришные решение никогда не доводятся до ума, я не могу быть личным консультантом
для Вас есть вариант - заказать этот несложный проект у ребят
http://forum.arduino.ua/viewtopic.php?id=1069
либо помочь Пете )
у меня племмяник нынче на химии в Минске, денег эти процедуры тянут немеренно, стране нынче не до этих малышей ( это жесть как их много ((( ), потому люд подлючаю не байдужий. Сложно боротся когда нужно думать чем оплатить транш в Пт когда на счетах 10% от счета ( но эт дело такое...
просто поделитесь если совсем туго
группа https://www.facebook.com/groups/594145280779388/
я вечером сделаю прототип, 25 Гц регулировка энкодером и терминалкой
какая нужна точность установки ? в абсолютных % , никаких относительных и дополнительных погрешностей.
- yarikne
- 2017-05-08 10:43:42
... ничего не понял, даташит от чего? Что именно правилось?
Прошу прощения, но я пока очень далек от программирования пока. Если не сложно, можно чуток доходчивые, подробнее.
- NoName
- 2017-05-08 09:27:53
по даташиту сами проверите, правил servo.cpp на уровне догадок
old PRESCALER 8
static void InitISR_handler()
{
__disable_irq();
NRF_TIMER1->TASKS_STOP = 1;
NRF_TIMER1->MODE = TIMER_MODE_MODE_Timer;
NRF_TIMER1->PRESCALER = 3;
NRF_TIMER1->BITMODE = TIMER_BITMODE_BITMODE_16Bit;
NRF_TIMER1->TASKS_CLEAR = 1;
NRF_TIMER1->CC[0] = (uint32_t)(VARIANT_MCK/8/1000); // 1ms
NRF_TIMER1->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] = 0;
NRF_TIMER1->INTENSET = (TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE0_Set << TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE0_Pos);
NVIC_SetPriority(TIMER1_IRQn, 1);
NVIC_EnableIRQ(TIMER1_IRQn);
__enable_irq();
NRF_TIMER1->TASKS_START = 1;
}
new old PRESCALER 16?
#define usToTicks(_us) (( clockCyclesPerMicrosecond()* _us) / 16) // converts microseconds to tick (assumes prescale of 8) // 12 Aug 2009
#define ticksToUs(_ticks) (( (unsigned)_ticks * 16)/ clockCyclesPerMicrosecond() ) // converts from ticks back to microseconds
static void InitISR_handler()
{
__disable_irq();
NRF_TIMER1->TASKS_STOP = 1;
NRF_TIMER1->MODE = TIMER_MODE_MODE_Timer;
NRF_TIMER1->PRESCALER = 4;
NRF_TIMER1->BITMODE = TIMER_BITMODE_BITMODE_16Bit;
NRF_TIMER1->TASKS_CLEAR = 1;
NRF_TIMER1->CC[0] = (uint32_t)(VARIANT_MCK/16/1000); // 1ms
NRF_TIMER1->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] = 0;
NRF_TIMER1->INTENSET = (TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE0_Set << TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE0_Pos);
NVIC_SetPriority(TIMER1_IRQn, 1);
NVIC_EnableIRQ(TIMER1_IRQn);
__enable_irq();
NRF_TIMER1->TASKS_START = 1;
}- NoName
- 2017-05-08 09:21:57
потолок 0xFFFF 32768 ) это ведь логично мы ведь о 8 битнике говорим, забылся
нужно найти делитель таймера и тогда сможете пользоваться
- yarikne
- 2017-05-07 21:42:04
Загрузил вот такое:
/*
Controlling a servo position using a potentiometer (variable resistor)
by Michal Rinott <http://people.interaction-ivrea.it/m.rinott>
modified on 8 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Knob
*/
#include <Servo.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x3F, 16, 2);
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int potpin = 0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer
int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
lcd.begin();
}
void loop() {
val = analogRead(potpin); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023)
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
myservo.write(val); // sets the servo position according to the scaled value
delay(15); // waits for the servo to get there
lcd.print("TEMP: ");
lcd.print(val); // отображение температуры
lcd.print("C ");
lcd.print(val); // отображение температуры
lcd.print("V ");
lcd.setCursor(0,1); // перевод курсора на следующую сторку
lcd.print("FANS: ");
lcd.print(val); // отображение скорости вращения вентилятора
lcd.print("%");
delay(200);
lcd.clear();
}На скорую руку собрал схемку - не работает. Осцила дома нет... ![]()
Но понять охота - подцепил динамик параллельно выходу с транзистора - на слух частота высоковата, анализаторы в андроид приложениях показывают 800 гц, могут врать конечно...
мой Servo.h
/*
Servo.h - Interrupt driven Servo library for Arduino using 16 bit timers- Version 2
Copyright (c) 2009 Michael Margolis. All right reserved.
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*/
/*
A servo is activated by creating an instance of the Servo class passing
the desired pin to the attach() method.
The servos are pulsed in the background using the value most recently
written using the write() method.
Note that analogWrite of PWM on pins associated with the timer are
disabled when the first servo is attached.
Timers are seized as needed in groups of 12 servos - 24 servos use two
timers, 48 servos will use four.
The sequence used to sieze timers is defined in timers.h
The methods are:
Servo - Class for manipulating servo motors connected to Arduino pins.
attach(pin ) - Attaches a servo motor to an i/o pin.
attach(pin, min, max ) - Attaches to a pin setting min and max values in microseconds
default min is 544, max is 2400
write() - Sets the servo angle in degrees. (invalid angle that is valid as pulse in microseconds is treated as microseconds)
writeMicroseconds() - Sets the servo pulse width in microseconds
read() - Gets the last written servo pulse width as an angle between 0 and 180.
readMicroseconds() - Gets the last written servo pulse width in microseconds. (was read_us() in first release)
attached() - Returns true if there is a servo attached.
detach() - Stops an attached servos from pulsing its i/o pin.
*/
#ifndef Servo_h
#define Servo_h
#include <inttypes.h>
/*
* Defines for 16 bit timers used with Servo library
*
* If _useTimerX is defined then TimerX is a 16 bit timer on the current board
* timer16_Sequence_t enumerates the sequence that the timers should be allocated
* _Nbr_16timers indicates how many 16 bit timers are available.
*/
// Architecture specific include
#if defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_AVR)
#include "avr/ServoTimers.h"
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAM)
#include "sam/ServoTimers.h"
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD)
#include "samd/ServoTimers.h"
#else
#error "This library only supports boards with an AVR, SAM or SAMD processor."
#endif
#define Servo_VERSION 2 // software version of this library
#define MIN_PULSE_WIDTH 544 // the shortest pulse sent to a servo
#define MAX_PULSE_WIDTH 2400 // the longest pulse sent to a servo
#define DEFAULT_PULSE_WIDTH 1500 // default pulse width when servo is attached
#define REFRESH_INTERVAL 40000 // minumim time to refresh servos in microseconds
#define SERVOS_PER_TIMER 12 // the maximum number of servos controlled by one timer
#define MAX_SERVOS (_Nbr_16timers * SERVOS_PER_TIMER)
#define INVALID_SERVO 255 // flag indicating an invalid servo index
typedef struct {
uint8_t nbr :6 ; // a pin number from 0 to 63
uint8_t isActive :1 ; // true if this channel is enabled, pin not pulsed if false
} ServoPin_t ;
typedef struct {
ServoPin_t Pin;
volatile unsigned int ticks;
} servo_t;
class Servo
{
public:
Servo();
uint8_t attach(int pin); // attach the given pin to the next free channel, sets pinMode, returns channel number or 0 if failure
uint8_t attach(int pin, int min, int max); // as above but also sets min and max values for writes.
void detach();
void write(int value); // if value is < 200 its treated as an angle, otherwise as pulse width in microseconds
void writeMicroseconds(int value); // Write pulse width in microseconds
int read(); // returns current pulse width as an angle between 0 and 180 degrees
int readMicroseconds(); // returns current pulse width in microseconds for this servo (was read_us() in first release)
bool attached(); // return true if this servo is attached, otherwise false
private:
uint8_t servoIndex; // index into the channel data for this servo
int8_t min; // minimum is this value times 4 added to MIN_PULSE_WIDTH
int8_t max; // maximum is this value times 4 added to MAX_PULSE_WIDTH
};
#endifво вложении фотка осциллограммы, это то, что хотелось бы получить.
И фотки процесса )))
намерил подручными средствами 138гц
вернул в зад #define REFRESH_INTERVAL 20000 - получил 50гц
- NoName
- 2017-05-07 18:05:53
ваш вариант PWM servo->writeMicroseconds
пример с энкодером я показал ранее. успехов.
- yarikne
- 2017-05-07 11:04:22
Все верно, я имею ввиду скважность. На счёт обратной связи, это я перепутал, неправильно понял.
Если не сложно, кто сталкивался с серво, дайте пример программки , желательно с управлением скважностью через терминал.
И может расскажите пару слов о программных таймерах.
- NoName
- 2017-05-07 08:56:41
#define Servo_VERSION 2 // software version of this library
#define MIN_PULSE_WIDTH 544 // the shortest pulse sent to a servo
#define MAX_PULSE_WIDTH 2400 // the longest pulse sent to a servo
#define DEFAULT_PULSE_WIDTH 1500 // default pulse width when servo is attached
#define REFRESH_INTERVAL 20000 // minumim time to refresh servos in microseconds
#define SERVOS_PER_TIMER 12 // the maximum number of servos controlled by one timer
1000000/REFRESH_INTERVAL
1000000/20000 = 50 Hz
я предпологаю что
#define REFRESH_INTERVAL 40000 // minumim time to refresh servos in microseconds
даст 25 Гц несущую
и возможно автор имеет в виду не частотное управление и именно коефичиент заполнения на 25 Гц 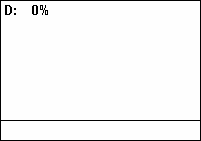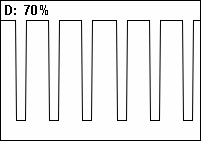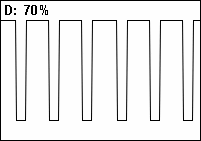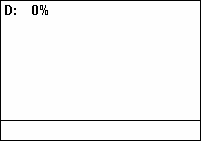
тогда writeMicroseconds() и будет работать
"обратная связь?"
это наверно что то совсем специальное
у меня в файле ничего такого нет
C:\Program Files (x86)\Arduino\libraries\Servo\src\Servo.h
The methods are:
Servo - Class for manipulating servo motors connected to Arduino pins.
attach(pin ) - Attaches a servo motor to an i/o pin.
attach(pin, min, max ) - Attaches to a pin setting min and max values in microseconds
default min is 544, max is 2400
write() - Sets the servo angle in degrees. (invalid angle that is valid as pulse in microseconds is treated as microseconds)
writeMicroseconds() - Sets the servo pulse width in microseconds
read() - Gets the last written servo pulse width as an angle between 0 and 180.
readMicroseconds() - Gets the last written servo pulse width in microseconds. (was read_us() in first release)
attached() - Returns true if there is a servo attached.
detach() - Stops an attached servos from pulsing its i/o pin.
насчет шокера - не шучу, главное в цепи и корпус не бить а то выгорит ваша железяка.
есть вариант попроще, пьезо зажигалка 1 мм пробоя ~ 1КB ЭМИ тоже есть в наличии ) тестируйте только не в цепи, а то будет "кака"
25Hz маленькая частота, можно и напрограмных таймерах сделать.